Page 19 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 19
S.Baizakov, A.Tulepbekova, A.Assenova: Regulatory policy of Kazakhstan: problems
and perspectives
One of the main objectives of the RIA procedure is to determine the minimum
cost of the introduced regulation. Each regulation is, to some extent, associated with
costs, both for business and for the authorities themselves. When calculating the
benefits and costs, various methods are used. These methods allow you to compare
scenarios and options. When calculating costs and benefits, you can combine these
methods. Each method has its pros and cons. The choice of method depends on the
purpose of the analysis of the regulatory impact and justification of the actions.
Often acts are passed through RIAs, in the basis of which there are no calculations,
the developers of which did not project the consequences of their proposed
standards. As a result, a negative conclusion is made, RIA projects are sent for
revision and, for objective reasons, making a decision is delayed. It is necessary to
develop an algorithm and to teach in advance to count and plan all the costs that the
draft act entails. This is not only an ideology, but also specific methods of work that
are important and need to be implemented (Table 1).
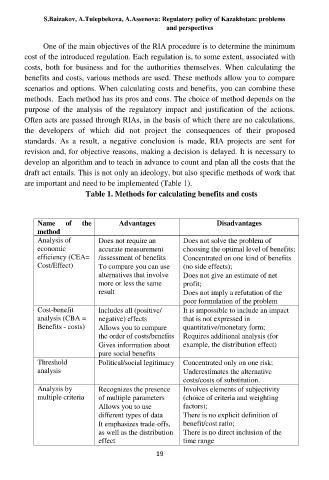
Table 1. Methods for calculating benefits and costs
Name of the Advantages Disadvantages
method
Analysis of Does not require an Does not solve the problem of
economic accurate measurement choosing the optimal level of benefits;
efficiency (CEA= /assessment of benefits Concentrated on one kind of benefits
Cost/Effect) To compare you can use (no side effects);
alternatives that involve Does not give an estimate of net
more or less the same profit;
result Does not imply a refutation of the
poor formulation of the problem
Cost-benefit Includes all (positive/ It is impossible to include an impact
analysis (CBA = negative) effects that is not expressed in
Benefits - costs) Allows you to compare quantitative/monetary form;
the order of costs/benefits Requires additional analysis (for
Gives information about example, the distribution effect)
pure social benefits
Threshold Political/social legitimacy Concentrated only on one risk;
analysis Underestimates the alternative
costs/costs of substitution.
Analysis by Recognizes the presence Involves elements of subjectivity
multiple criteria of multiple parameters (choice of criteria and weighting
Allows you to use factors);
different types of data There is no explicit definition of
It emphasizes trade-offs, benefit/cost ratio;
as well as the distribution There is no direct inclusion of the
effect time range
19