Page 10 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 10
THE JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC SCIENCES: THEORY AND PRACTICE, V.78, # 2, 2021, pp. 4-16
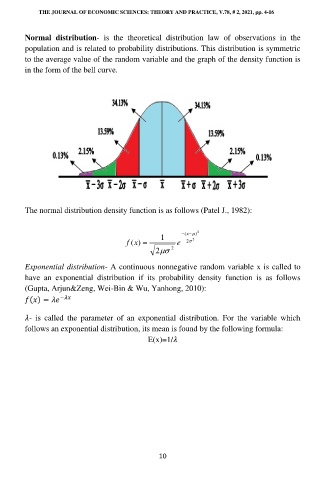
Normal distribution- is the theoretical distribution law of observations in the
population and is related to probability distributions. This distribution is symmetric
to the average value of the random variable and the graph of the density function is
in the form of the bell curve.
The normal distribution density function is as follows (Patel J., 1982):
− ( −x ) 2
1
f (x ) = e 2 2
2 2
Exponential distribution- A continuous nonnegative random variable x is called to
have an exponential distribution if its probability density function is as follows
(Gupta, Arjun&Zeng, Wei-Bin & Wu, Yanhong, 2010):
( ) = −
- is called the parameter of an exponential distribution. For the variable which
follows an exponential distribution, its mean is found by the following formula:
E(x)=1/
10