Page 52 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 52
THE JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC SCIENCES: THEORY AND PRACTICE, V.82, # 2, 2025, pp. 32-60
Inflation dynamics are regime-sensitive; for instance, INFLATION(-2) is significantly
negative (z ≈ -2.72), pointing to corrective mechanisms such as monetary policy or adaptive
expectations. Unemployment exhibits delayed reactions, notably under regime 2, where
CHOMAGE(-1) significantly correlates with inflation (z ≈ 2.68), reflecting labor market
stress amid price instability. Residual standard deviations (SIGMA) confirm higher
volatility in regime 2, especially for unemployment and inflation. The error covariance
matrix reveals significant positive correlations between LPIB and LDEP, consistent with
fiscally-driven growth dynamics. The model’s robustness is supported by a residual
covariance determinant of 1.25e-07, log-likelihood of 82.24, and favorable Akaike and
Schwarz information criteria.
Impulse Response Analysis
Using Cholesky orthogonalization with degrees-of-freedom adjustment, the impulse
responses reveal substantial regime-dependent differences. In the sTable regime, a positive
public spending shock leads to a moderate and gradual increase in real GDP, temporary
inflationary pressure, and a slight reduction in unemployment—patterns consistent with
Keynesian multipliers. Conversely, in the crisis or volatile regime, the same shock results
in weaker GDP responses, sharper inflationary spikes, and an ambiguous or delayed impact
on unemployment. These findings align with Auerbach and Gorodnichenko (2012),
highlighting that fiscal multipliers are state-dependent—more effective in sTable periods
and significantly constrained during recessions or turbulent conditions.
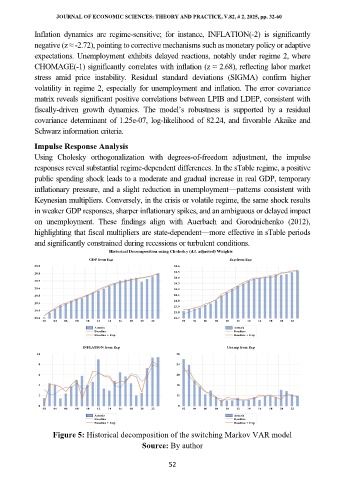
Historical Decomposition using Cholesky (d.f. adjusted) Weights
GDP from Exp Exp from Exp
29.9 24.6
24.5
29.8
24.4
29.7
24.3
29.6 24.2
29.5 24.1
24.0
29.4
23.9
29.3
23.8
29.2 23.7
02 04 06 08 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 02 04 06 08 10 12 14 16 18 20 22
Actuals Actuals
Baseline Baseline
Baseline + Exp Baseline + Exp
INFLATION from Exp Unemp from Exp
10 28
8 24
6 20
4 16
2 12
0 8
02 04 06 08 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 02 04 06 08 10 12 14 16 18 20 22
Actuals Actuals
Baseline Baseline
Baseline + Exp Baseline + Exp
Figure 5: Historical decomposition of the switching Markov VAR model
Source: By author
52