Page 98 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 98
Yang Zhifang, Zhang Jieqian, Rudnák Ildikó: China-Hungary Trade Relations
Under The Belt And Road Initiative
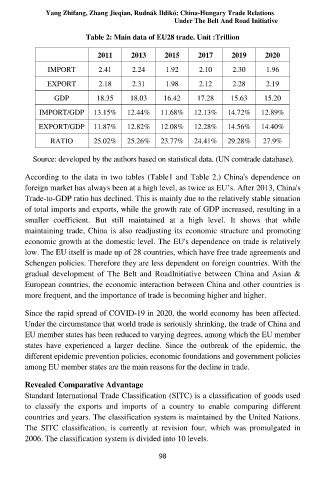
Table 2: Main data of EU28 trade. Unit :Trillion
2011 2013 2015 2017 2019 2020
IMPORT 2.41 2.24 1.92 2.10 2.30 1.96
EXPORT 2.18 2.31 1.98 2.12 2.28 2.19
GDP 18.35 18.03 16.42 17.28 15.63 15.20
IMPORT/GDP 13.15% 12.44% 11.68% 12.13% 14.72% 12.89%
EXPORT/GDP 11.87% 12.82% 12.08% 12.28% 14.56% 14.40%
RATIO 25.02% 25.26% 23.77% 24.41% 29.28% 27.9%
Source: developed by the authors based on statistical data. (UN comtrade database).
According to the data in two tables (Table1 and Table 2.) China's dependence on
foreign market has always been at a high level, as twice as EU’s. After 2013, China's
Trade-to-GDP ratio has declined. This is mainly due to the relatively stable situation
of total imports and exports, while the growth rate of GDP increased, resulting in a
smaller coefficient. But still maintained at a high level. It shows that while
maintaining trade, China is also readjusting its economic structure and promoting
economic growth at the domestic level. The EU's dependence on trade is relatively
low. The EU itself is made up of 28 countries, which have free trade agreements and
Schengen policies. Therefore they are less dependent on foreign countries. With the
gradual development of The Belt and RoadInitiative between China and Asian &
European countries, the economic interaction between China and other countries is
more frequent, and the importance of trade is becoming higher and higher.
Since the rapid spread of COVID-19 in 2020, the world economy has been affected.
Under the circumstance that world trade is seriously shrinking, the trade of China and
EU member states has been reduced to varying degrees, among which the EU member
states have experienced a larger decline. Since the outbreak of the epidemic, the
different epidemic prevention policies, economic foundations and government policies
among EU member states are the main reasons for the decline in trade.
Revealed Comparative Advantage
Standard International Trade Classification (SITC) is a classification of goods used
to classify the exports and imports of a country to enable comparing different
countries and years. The classification system is maintained by the United Nations.
The SITC classification, is currently at revision four, which was promulgated in
2006. The classification system is divided into 10 levels.
98