Page 17 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 17
Aboubaker Khoualed, Taher Makhloufi, Ahmed Makhloufi, Elyas Luqman: The Impact
of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) on Economic Development: The Case of Algeria
Diagnostic Tests for the FARDL Model
To validate the model's results, it must undergo a series of diagnostic tests as follows:
Actual and Estimated Values
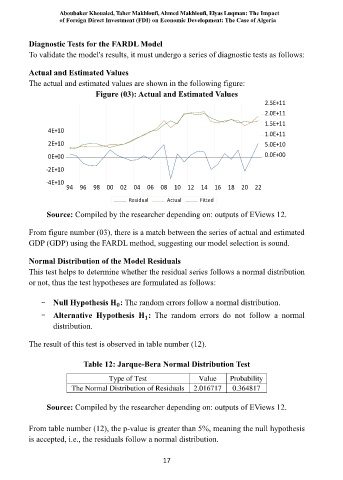
The actual and estimated values are shown in the following figure:
Figure (03): Actual and Estimated Values
2.5E+11
2.0E+11
1.5E+11
4E+10
1.0E+11
2E+10 5.0E+10
0E+00 0.0E+00
-2E+10
-4E+10
94 96 98 00 02 04 06 08 10 12 14 16 18 20 22
Residual Actual Fitted
Source: Compiled by the researcher depending on: outputs of EViews 12.
From figure number (03), there is a match between the series of actual and estimated
GDP (GDP) using the FARDL method, suggesting our model selection is sound.
Normal Distribution of the Model Residuals
This test helps to determine whether the residual series follows a normal distribution
or not, thus the test hypotheses are formulated as follows:
- Null Hypothesis : The random errors follow a normal distribution .
- Alternative Hypothesis : The random errors do not follow a normal
distribution .
The result of this test is observed in table number (12).
Table 12: Jarque-Bera Normal Distribution Test
Type of Test Value Probability
The Normal Distribution of Residuals 2.016717 0.364817
Source: Compiled by the researcher depending on: outputs of EViews 12.
From table number (12), the p-value is greater than 5%, meaning the null hypothesis
is accepted, i.e., the residuals follow a normal distribution.
17