Page 111 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 111
Fettouche Fatma: Influence of Human Capital On Employment In China Standard
Analytical Study
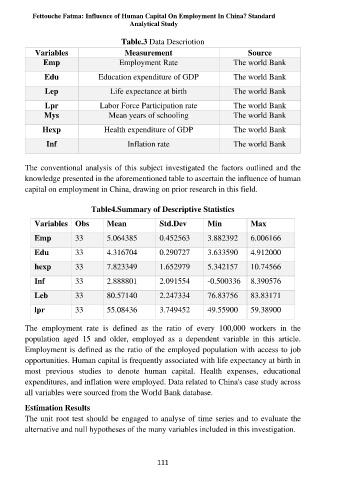
Table.3 Data Descriotion
Variables Measurement Source
Emp Employment Rate The world Bank
Edu Education expenditure of GDP The world Bank
Lep Life expectance at birth The world Bank
Lpr Labor Force Participation rate The world Bank
Mys Mean years of schooling The world Bank
Hexp Health expenditure of GDP The world Bank
Inf Inflation rate The world Bank
The conventional analysis of this subject investigated the factors outlined and the
knowledge presented in the aforementioned table to ascertain the influence of human
capital on employment in China, drawing on prior research in this field.
Table4.Summary of Descriptive Statistics
Variables Obs Mean Std.Dev Min Max
Emp 33 5.064385 0.452563 3.882392 6.006166
Edu 33 4.316704 0.290727 3.633590 4.912000
hexp 33 7.823349 1.652979 5.342157 10.74566
Inf 33 2.888801 2.091554 -0.500336 8.390576
Leb 33 80.57140 2.247334 76.83756 83.83171
lpr 33 55.08436 3.749452 49.55900 59.38900
The employment rate is defined as the ratio of every 100,000 workers in the
population aged 15 and older, employed as a dependent variable in this article.
Employment is defined as the ratio of the employed population with access to job
opportunities. Human capital is frequently associated with life expectancy at birth in
most previous studies to denote human capital. Health expenses, educational
expenditures, and inflation were employed. Data related to China's case study across
all variables were sourced from the World Bank database.
Estimation Results
The unit root test should be engaged to analyse of time series and to evaluate the
alternative and null hypotheses of the many variables included in this investigation.
111