Page 25 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 25
Aimene Farid, Bahi Nawel:Operational Risk Estimation Using the Value-at-Risk (VAR)
Method: Case Study of the External Bank of Algeria (EBA)
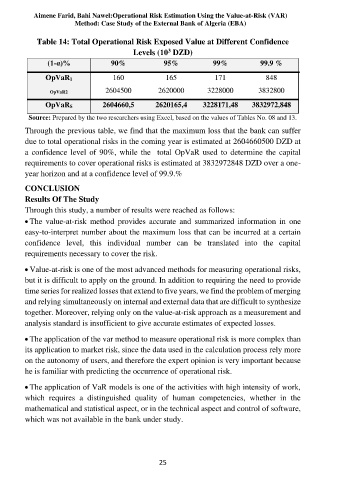
Table 14: Total Operational Risk Exposed Value at Different Confidence
Levels (10 DZD)
3
(1-α)% 90% 95% 99% 99.9 %
OpVaR1 160 165 171 848
OpVaR2 2604500 2620000 3228000 3832800
OpVaRS 2604660,5 2620165,4 3228171,48 3832972,848
Source: Prepared by the two researchers using Excel, based on the values of Tables No. 08 and 13.
Through the previous table, we find that the maximum loss that the bank can suffer
due to total operational risks in the coming year is estimated at 2604660500 DZD at
a confidence level of 90%, while the total OpVaR used to determine the capital
requirements to cover operational risks is estimated at 3832972848 DZD over a one-
year horizon and at a confidence level of 99.9.%
CONCLUSION
Results Of The Study
Through this study, a number of results were reached as follows:
• The value-at-risk method provides accurate and summarized information in one
easy-to-interpret number about the maximum loss that can be incurred at a certain
confidence level, this individual number can be translated into the capital
requirements necessary to cover the risk.
• Value-at-risk is one of the most advanced methods for measuring operational risks,
but it is difficult to apply on the ground. In addition to requiring the need to provide
time series for realized losses that extend to five years, we find the problem of merging
and relying simultaneously on internal and external data that are difficult to synthesize
together. Moreover, relying only on the value-at-risk approach as a measurement and
analysis standard is insufficient to give accurate estimates of expected losses.
• The application of the var method to measure operational risk is more complex than
its application to market risk, since the data used in the calculation process rely more
on the autonomy of users, and therefore the expert opinion is very important because
he is familiar with predicting the occurrence of operational risk.
• The application of VaR models is one of the activities with high intensity of work,
which requires a distinguished quality of human competencies, whether in the
mathematical and statistical aspect, or in the technical aspect and control of software,
which was not available in the bank under study.
25