Page 58 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 58
THE JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC SCIENCES: THEORY AND PRACTICE, V.82, # 1, 2025, pp. 52-69
approaches focus on investigating how, why, and under what conditions these
relationships occur. In this regard, the concepts of mediation and moderation are
analytical approaches widely used in social sciences and applied statistics. Mediation
analysis examines whether the effect of one variable (independent variable – X) on
another variable (dependent variable – Y) is mediated through a third variable
(mediator – M). This approach aims to clarify the mechanisms behind the cause-effect
relationship. For example, indirect effect is studied through the sequence X → M →
Y. If the effect of X on Y is mediated by the variable M, this effect is considered a
"mediation effect." Moderation analysis examines whether the relationship between
X and Y changes depending on the level of another variable (Z). This variable is called
a moderator. If the variable Z changes the direction or strength of the relationship,
then Z has a moderating role. This model is usually analyzed through interaction
effects and answers the question: "Does the effect of X on Y change due to Z?"
The PROCESS macro introduced by Andrew F. Hayes (2018), used in this article, is
a tool that simplifies the implementation of mediation, moderation, and conditional
process models in SPSS and other statistical programs. Macro offers more than 90
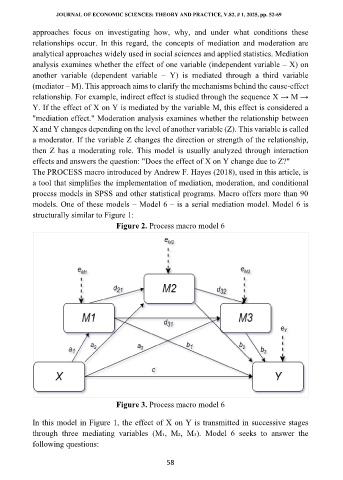
models. One of these models – Model 6 – is a serial mediation model. Model 6 is
structurally similar to Figure 1:
Figure 2. Process macro model 6
Figure 3. Process macro model 6
In this model in Figure 1, the effect of X on Y is transmitted in successive stages
through three mediating variables (M₁, M₂, M₃). Model 6 seeks to answer the
following questions:
58