Page 78 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 78
THE JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC SCIENCES: THEORY AND PRACTICE, V.82, # 1, 2025, pp. 70-88
The distribution of healthcare services based on the type of institution shows that
58.3% (n = 70) of services were provided by public medical institutions, while 41.7%
(n = 50) were delivered by private medical institutions, totaling 120 cases. Regarding
the types of healthcare services received, the majority were hospital services,
accounting for 52.2% (n = 71) of cases. Polyclinics provided 24.3% (n = 33) of the
services, followed by medical stations at 7.4% (n = 10). Other service types included
outpatient and inpatient services (5.1%, n = 7), doctor’s offices (5.1%, n = 7),
outpatient services only (4.4%, n = 6), and hygiene and epidemiology centers (1.5%,
n = 2). The total number of healthcare service instances recorded was 136.
Research Model And Hypotheses
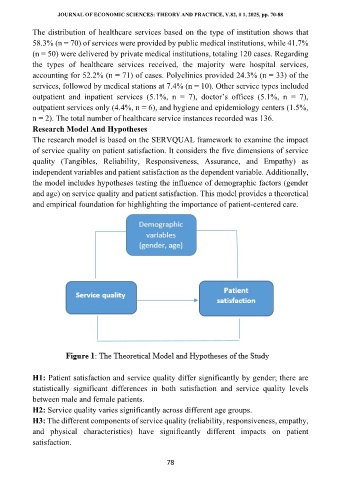
The research model is based on the SERVQUAL framework to examine the impact
of service quality on patient satisfaction. It considers the five dimensions of service
quality (Tangibles, Reliability, Responsiveness, Assurance, and Empathy) as
independent variables and patient satisfaction as the dependent variable. Additionally,
the model includes hypotheses testing the influence of demographic factors (gender
and age) on service quality and patient satisfaction. This model provides a theoretical
and empirical foundation for highlighting the importance of patient-centered care.
H1: Patient satisfaction and service quality differ significantly by gender; there are
statistically significant differences in both satisfaction and service quality levels
between male and female patients.
H2: Service quality varies significantly across different age groups.
H3: The different components of service quality (reliability, responsiveness, empathy,
and physical characteristics) have significantly different impacts on patient
satisfaction.
78