Page 99 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 99
THE JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC SCIENCES: THEORY AND PRACTICE
Hence, banking system of Ukraine fulfils funds transformation functions
inefficiently and by itself imposes risk for financial stability.
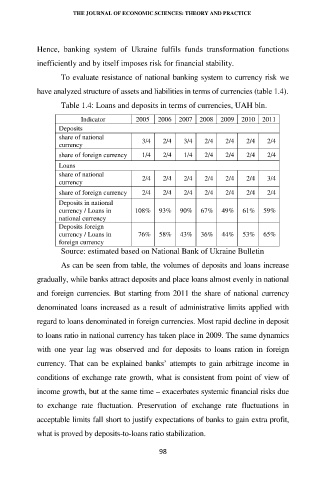
To evaluate resistance of national banking system to currency risk we
have analyzed structure of assets and liabilities in terms of currencies (table 1.4).
Table 1.4: Loans and deposits in terms of currencies, UAH bln.
Indicator 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011
Deposits
share of national
currency 3/4 2/4 3/4 2/4 2/4 2/4 2/4
share of foreign currency 1/4 2/4 1/4 2/4 2/4 2/4 2/4
Loans
share of national
currency 2/4 2/4 2/4 2/4 2/4 2/4 3/4
share of foreign currency 2/4 2/4 2/4 2/4 2/4 2/4 2/4
Deposits in national
currency / Loans in 108% 93% 90% 67% 49% 61% 59%
national currency
Deposits foreign
currency / Loans in 76% 58% 43% 36% 44% 53% 65%
foreign currency
Source: estimated based on National Bank of Ukraine Bulletin
As can be seen from table, the volumes of deposits and loans increase
gradually, while banks attract deposits and place loans almost evenly in national
and foreign currencies. But starting from 2011 the share of national currency
denominated loans increased as a result of administrative limits applied with
regard to loans denominated in foreign currencies. Most rapid decline in deposit
to loans ratio in national currency has taken place in 2009. The same dynamics
with one year lag was observed and for deposits to loans ration in foreign
currency. That can be explained banks’ attempts to gain arbitrage income in
conditions of exchange rate growth, what is consistent from point of view of
income growth, but at the same time – exacerbates systemic financial risks due
to exchange rate fluctuation. Preservation of exchange rate fluctuations in
acceptable limits fall short to justify expectations of banks to gain extra profit,
what is proved by deposits-to-loans ratio stabilization.
98