Page 18 - Azerbaijan State University of Economics
P. 18
THE JOURNAL OF ECONOMIC SCIENCES: THEORY AND PRACTICE, V.81, # 2, 2024, pp. 4-29
n
1
2
= √∑ (V − μ)
N i
i=1
As a first stage, we calculate the standard deviation of loss values, and the following
table shows this:
Table 05: Calculation of Average and Standard Deviation of Loss Values
(Thousand DZD)
Loss Value Vi − / ( − )
V1 50 30,00 900
V2 4 (16, 00) 256
V3 12 (8, 00) 64
V4 44 24,00 576
V5 2 (18:00) 324
V6 36 16,00 256
V7 11 (9, 00 81
V8 18 ≤ 2.00 4
V9 3 (17, 00) 289
Total 180 - 2 750,00
µ 20 σ² 305
Σ 17.48
Source: Prepared by the two researchers using Excel, based on the values of Table 02.
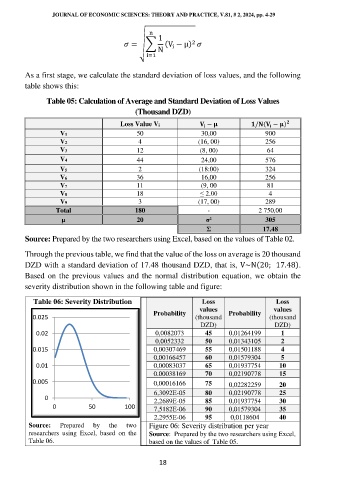
Through the previous table, we find that the value of the loss on average is 20 thousand
DZD with a standard deviation of 17.48 thousand DZD, that is, V~N(20; 17.48).
Based on the previous values and the normal distribution equation, we obtain the
severity distribution shown in the following table and figure:
Table 06: Severity Distribution Loss Loss
values values
Probability Probability
0.025 (thousand (thousand
DZD) DZD)
0.02 0,0082073 45 0,01264199 1
0,0052332 50 0,01343105 2
0.015 0,00307469 55 0,01501188 4
0,00166457 60 0,01579304 5
0.01 0,00083037 65 0,01937754 10
0.00038169 70 0,02190778 15
0.005 0,00016166 75 0,02282259 20
6,3092E-05 80 0,02190778 25
0
2,2689E-05 85 0,01937754 30
0 50 100 7,5182E-06 90 0,01579304 35
2,2955E-06 95 0,0118604 40
Source: Prepared by the two Figure 06: Severity distribution per year
researchers using Excel, based on the Source: Prepared by the two researchers using Excel,
Table 06. based on the values of Table 05.
18